Properties of polygons
Introduction
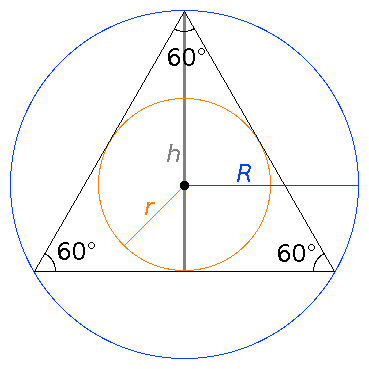
I've collected here lengths, areas and angles regarding regular polygons. (In a regular polygon, all angles are equal and all sides are the same length.)
General formulas
General formulas for regular n-gons (regular polygons with n sides), with each side of length one:
| circumradius | R = √(r2 + 1 / 4) = 1 / (2 × sin(180° / n)) |
|---|---|
| inradius | r = √(R2 − 1 / 4) = 1 / (2 × tan(180° / n)) |
| area | A = nr / 2 = n × R2 × sin(360° / n) / 2 = n / (4 × tan(180° / n)) |
| height for even n | h = 2r |
| height for odd n | h = R + r = tan((n − 1) / n × 90°) / 2 |
| internal angles | (n − 2) / n × 180° |
Specific polygons
The table shows the name and exact values for some regular n-gons, with each side of length one:
| n | Name | Circumradius R | Inradius r | Area A | Height h | Internal angles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | triangle | √3 / 3 | √3 / 6 | √3 / 4 | √3 / 2 | 60° |
| 4 | square | √2 / 2 | 1 / 2 | 1 | 1 | 90° |
| 5 | pentagon | √(50 + 10√5) / 10 | √(25 + 10√5) / 10 | √(25 + 10√5) / 4 | √(5 + 2√5) / 2 | 108° |
| 6 | hexagon | 1 | √3 / 2 | 3√3 / 2 | √3 | 120° |
| 8 | octagon | √(4 + 2√2) / 2 = 1 / √(2 − √2) | (1 + √2) / 2 | 2 + 2√2 | 1 + √2 | 135° |
| 10 | decagon | (1 + √5) / 2 | √(5 + 2√5) / 2 | 5√(5 + 2√5) / 2 | √(5 + 2√5) | 144° |
| 12 | dodecagon | (√6 + √2) / 2 = √(2 + √3) | (2 + √3) / 2 | 6 + 3√3 | 2 + √3 | 150° |
| 15 | pentadecagon | (√3 + √(5 + 2√5)) / 2 | (√3 + √15 + √(10 + 2√5)) / 4 | 15r / 2 | (3√3 + √15 + √(50 + 22√5)) / 4 | 156° |
| 16 | hexadecagon | √(8 + 4√2 + 2√(20+14√2)) / 2 = 1 / √(2 − √(2 + √2)) |
(1 + √2 + √(4 + 2√2)) / 2 | 8r | 2r | 157.5° |
| 20 | icosagon | √(12 + 4√5 + 2√(50 + 22√5)) / 2 = 2 / √(8 − 2√(10 + 2√5)) |
(1 + √5 + √(5 + 2√5)) / 2 | 10r | 2r | 162° |
| 24 | icositetragon | √(16 + 10√2 + 8√3 + 6√6) / 2 = 1 / √(2 − √(2 + √3)) |
(2 + √2 + √3 + √6) / 2 | 12r | 2r | 165° |
| 30 | triacontagon | (2 + √5 + √(15 + 6√5)) / 2 | (3√3 + √15 + √(50 + 22√5)) / 4 | 15r | 2r | 168° |
Sources:
- MathWorld: equilateral triangle, square, regular pentagon, regular hexagon, regular octagon, regular decagon, regular dodecagon, pentadecagon, hexadecagon, icosagon, icositetragon, triacontagon
- WolframAlpha
As triangles
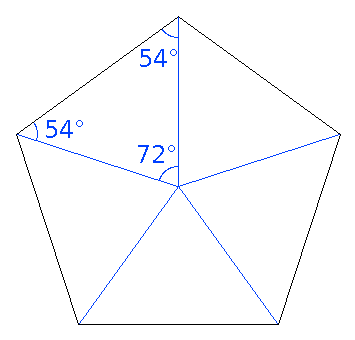
A regular n-gon can be split into n equal isosceles triangles which meet at the centre of the polygon (see image). The angle at the centre of the polygon is 360° / n. The other two angles are 180° minus that angle, divided by two, or (n − 2) / n × 90° each.