Properties of polygons and polyhedra
Introduction
This is a list of distances, areas and angles regarding some 2D and 3D shapes.
Polygons
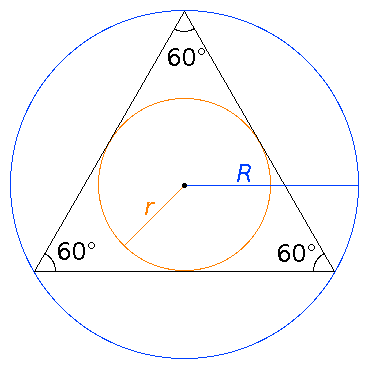
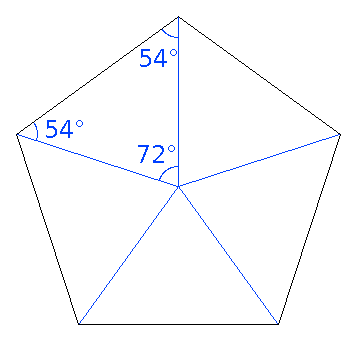
The table shows the name, circumradius R and inradius r for various regular polygons (all angles equal) with n sides, each of length one. The first row after the headers (n=any) has general formulas that work with any such polygon.
| n | Name | Circumradius | Inradius |
|---|---|---|---|
| any | n-gon | 1 / (2 × sin(180° / n)) | 1 / (2 × tan(180° / n)) |
| 3 | triangle | √3 / 3 | √3 / 6 |
| 4 | square | √2 / 2 | 1 / 2 |
| 5 | pentagon | √((5 + √5) / 10) | √(25 + 10√5) / 10 |
| 6 | hexagon | 1 | √3 / 2 |
| 8 | octagon | 1 / √(2 − √2) | (1 + √2) / 2 |
| 10 | decagon | (1 + √5) / 2 | √(5 + 2√5) / 2 |
| 12 | dodecagon | (√6 + √2) / 2 | (2 + √3) / 2 |
| 15 | penta(kai)decagon | (√3 + √(5 + 2√5)) / 2 | √(7 + 2√5 + 2√(15 + 6√5)) / 2 |
| 16 | hexa(kai)decagon | 1 / √(2 − √(2 + √2)) | (1 + √2 + √(4 + 2√2)) / 2 |
| 20 | icosagon | 2 / √(8 − √(40 + 8√5)) | (1 + √5 + √(5 + 2√5)) / 2 |
| 24 | icosi(kai)tetragon | 1 / √(2 − √(2 + √3)) | (2 + √2 + √3 + √6) / 2 |
| 30 | triacontagon | (2 + √5 + √(15 + 6√5)) / 2 | 1 / (2√(7 − 2√5 − 2√(15 − 6√5))) |
| 32 | triaconta(kai)digon | 1 / √(2 − √(2 + √(2 + √2))) | √(1 / (2 − √(2 + √(2 + √2))) − 1 / 4) |
| 48 | tetraconta(kai)octagon | 1 / √(2 − √(2 + √(2 + √3))) | √(1 / (2 − √(2 + √(2 + √3))) − 1 / 4) |
| 60 | hexacontagon | 2 / √(8 − √3 − √15 − √(10 − 2√5)) | √(4 / (8 − √3 − √15 − √(10 − 2√5)) − 1 / 4) |
How R and r depend on each other:
- R = √(r2 + 1 / 4)
- r = √(R2 − 1 / 4)
Other properties of regular n-gons:
- area from number of sides and inradius: A = nr / 2 = n / (4 × tan(180° / n))
- internal angle between two sides: 180° × (n − 2) / n
- distance between two opposite vertices (for even n): 2R
- distance between centres of two opposite sides (for even n): 2r
- distance between vertex and centre of opposite side (for odd n): R + r
- distance between two different vertices that are adjacent to the same vertex (for n ≥ 4): 2 × cos(180° / n)
A regular n-gon can be split into n similar isosceles triangles which meet at the centre of the polygon (see image); each triangle has:
- two angles of 90° × (n − 2) / n and one of 360° / n
- two sides of length R and one of length 1
- height r
Polyhedra
Some regular polyhedra with edge length one.
Faces: e.g. 8×3+6×4 means 8 triangles and 6 squares. Circumradius, midradius and inradius: radius of circumsphere, midsphere and insphere, respectively; they touch each vertex, edge and face once, respectively.
| Name | Faces | Circumradius | Midradius | Inradius |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tetrahedron | 4×3 | √6 / 4 | √2 / 4 | √6 / 12 |
| octahedron | 8×3 | √2 / 2 | 1 / 2 | √6 / 6 |
| dodecahedron | 12×5 | (√3 + √15) / 4 | (3 + √5) / 4 | √((25 + 11√5) / 10) / 2 |
| icosahedron | 20×3 | √((5 + √5) / 2) / 2 | (1 + √5) / 4 | (3√3 + √15) / 12 |
Sources
- Wikipedia: category: polygons by the number of sides
- Wikipedia: Platonic solid
- Wolfram MathWorld: polygons
- WolframAlpha