How to build logic gates from other logic gates
Introduction
Here are formulas that tell you how to build various logic gates (e.g. three-input XOR) from two-input NAND gates only or from two-input NOR gates only.
Operands used on this page:
| Operand | Meaning |
|---|---|
| A, B, C, D | input bits of functions |
| T, U, V | temporary bits (if the value is needed more than once) |
Operators used on this page:
| Operator | Meaning |
|---|---|
| ¬ | bitwise NOT (1 input; e.g. ¬A) |
| ∧ | bitwise AND (2 inputs) |
| ⊼ | bitwise NAND (2 inputs) |
| ∨ | bitwise OR (2 inputs) |
| ⊽ | bitwise NOR (2 inputs) |
| ⊻ | bitwise XOR (2 inputs) |
| = | assignment of temporary bit (e.g. T = ¬A) |
¬ has the highest precedence and = the lowest. That is, T=¬A∧B means T=((¬A)∧B).
Diagram symbols for the NOT, NAND and NOR gates:
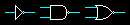
Truth table for the one-input gate:
| A | ¬A |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
Truth tables for the two-input gates; ¬(A⊻B) means A XNOR B:
| A | B | A∧B | A⊼B | A∨B | A⊽B | A⊻B | ¬(A⊻B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Notes:
- I found the formulas with this Python program (messy). The formulas are optimal (exhaustively searched) unless otherwise noted.
- The “Delay” column shows the maximum number of gates the signal must travel through.
- When there are many nested parentheses in a formula, square brackets are used for every third level starting from the inside. E.g. [((A∧B)∧C)∧D] means (((A∧B)∧C)∧D).
- De Morgan's laws:
- ¬(A∧B) = ¬A∨¬B
- ¬(A∨B) = ¬A∧¬B
1-input gates
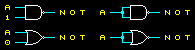
The truth table shows the output of the function for inputs A=0 and A=1.
| Formula | Truth table | NAND gates only | NOR gates only | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gates | Delay | Formula | Gates | Delay | Formula | ||
| ¬A | 1,0 | 1 | 1 | A⊼1 | 1 | 1 | A⊽0 |
| A⊼A | A⊽A | ||||||
2-input gates
The truth tables show the output of the function for all combinations of the inputs: A=0 and B=0; A=0 and B=1; A=1 and B=0; A=1 and B=1.
From now on, the “¬” operator is used in addition to “⊼” and “⊽” to reduce clutter.
The formulas have been grouped in pairs to highlight their similarities: e.g. changing all “⊼” operators to “⊽” in “(A⊼B) ⊼ (¬A⊼¬B)” turns the function from XNOR to XOR.
Order of inputs does not matter

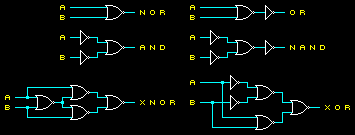
Swapping the values of A and B does not affect the result of these functions.
| Formula | A+B must equal | Truth table | NAND and NOT gates only | NOR and NOT gates only | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gates | Delay | Formula | Gates | Delay | Formula | |||
| A⊼B | 0 or 1 | 1,1,1,0 | 1 | 1 | A⊼B | 4 | 3 | ¬(¬A⊽¬B) |
| A⊽B | 0 | 1,0,0,0 | 4 | 3 | ¬(¬A⊼¬B) | 1 | 1 | A⊽B |
| A∧B | 2 | 0,0,0,1 | 2 | 2 | ¬(A⊼B) | 3 | 2 | ¬A⊽¬B |
| A∨B | 1 or 2 | 0,1,1,1 | 3 | 2 | ¬A⊼¬B | 2 | 2 | ¬(A⊽B) |
| A⊻B | 1 | 0,1,1,0 | 4 | 3 | T = A⊼B; (A⊼T)⊼(B⊼T) | 5 | 3 | (A⊽B) ⊽ (¬A⊽¬B) |
| ¬(A⊻B) | 0 or 2 | 1,0,0,1 | 5 | 3 | (A⊼B) ⊼ (¬A⊼¬B) | 4 | 3 | T = A⊽B; (A⊽T)⊽(B⊽T) |
Order of inputs matters
Swapping the values of A and B may affect the result of these functions.
| Formula | Truth table | NAND and NOT gates only | NOR and NOT gates only | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gates | Delay | Formula | Gates | Delay | Formula | ||
| A∨¬B | 1,0,1,1 | 2 | 2 | ¬A⊼B | 3 | 3 | ¬(A⊽¬B) |
| A∧¬B | 0,0,1,0 | 3 | 3 | ¬(A⊼¬B) | 2 | 2 | ¬A⊽B |
3-input gates
The truth tables show the output of the function for all combinations of the inputs: A=0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1; B=0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1; C=0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1.
Order of inputs does not matter
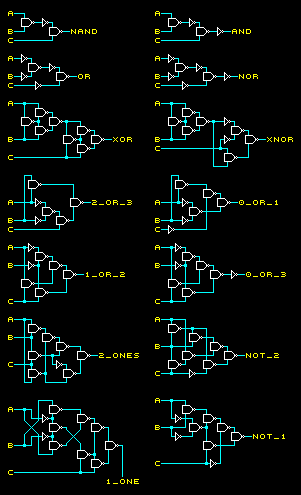
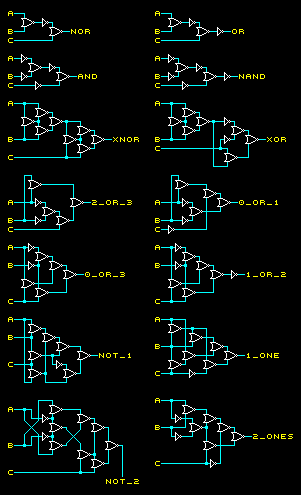
(TODO: redraw diagrams)
| Formula | A+B+C must equal | Truth table | NAND and NOT gates only | NOR and NOT gates only | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gates | Delay | Formula | Gates | Delay | Formula | |||
| ¬(A∧B∧C) | not 3 | 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0 | 3 | 3 | ¬(A⊼B)⊼C | 7 | 5 | ¬(¬(¬A⊽¬B) ⊽ ¬C) |
| ¬(A∨B∨C) | 0 | 1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0 | 7 | 5 | ¬(¬(¬A⊼¬B) ⊼ ¬C) | 3 | 3 | ¬(A⊽B)⊽C |
| A∧B∧C | 3 | 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1 | 4 | 4 | ¬(¬(A⊼B) ⊼ C) | 6 | 4 | ¬(¬A⊽¬B) ⊽ ¬C |
| A∨B∨C | not 0 | 0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 | 6 | 4 | ¬(¬A⊼¬B) ⊼ ¬C | 4 | 4 | ¬(¬(A⊽B) ⊽ C) |
| (A∧B)∨(A∧C)∨(B∧C) | 2 or 3 | 0,0,0,1,0,1,1,1 | 6 | 4 | (A⊼B) ⊼ ((¬A⊼¬B) ⊼ C) | 6 | 4 | (A⊽B) ⊽ ((¬A⊽¬B) ⊽ C) |
| ¬((A∧B)∨(A∧C)∨(B∧C)) | 0 or 1 | 1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0 | 7 | 3 | (¬A⊼¬B) ⊼ ((A⊼B)⊼¬C) | 7 | 3 | (¬A⊽¬B) ⊽ ((A⊽B)⊽¬C) |
| ¬(¬(A∨B∨C) ∨ (A∧B∧C)) | 1 or 2 | 0,1,1,1,1,1,1,0 | 7 | 4 | T = ¬B; ((¬A⊼T) ⊼ (A⊼C)) ⊼ (C⊼T) | 8 | 5 | T = ¬B; ¬[((¬A⊽T) ⊽ (A⊽C)) ⊽ (C⊽T)] |
| ¬(A∨B∨C) ∨ (A∧B∧C) | 0 or 3 | 1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1 | 8 | 5 | T = ¬B; ¬[((¬A⊼T) ⊼ (A⊼C)) ⊼ (C⊼T)] | 7 | 4 | T = ¬B; ((¬A⊽T) ⊽ (A⊽C)) ⊽ (C⊽T) |
| ¬((A⊻B)⊻C) ∧ (A∨B∨C) | 2 | 0,0,0,1,0,1,1,0 | 8 | 4 | T = A⊼C; U = B⊼C; [((A⊼B)⊼T) ⊼ U] ⊼ (T⊼¬U) | 9 | 5 | T = ¬A⊽¬B; [((A⊽B)⊽T) ⊽ ¬C] ⊽ (C⊽T) |
| ¬((A⊻B)⊻C) ∨ (A∧B∧C) | not 1 | 1,0,0,1,0,1,1,1 | 9 | 5 | T = ¬A⊼¬B; [((A⊼B)⊼T) ⊼ ¬C] ⊼ (C⊼T) | 8 | 4 | T = A⊽C; U = B⊽C; [((A⊽B)⊽T) ⊽ U] ⊽ (T⊽¬U) |
| (A⊻B)⊻C | 1 or 3 | 0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1 | 8 | 6 | T = A⊼B; U = (A⊼T)⊼(B⊼T); V = C⊼U; (C⊼V)⊼(U⊼V) | 8 | 6 | T = A⊽B; U = (A⊽T)⊽(B⊽T); V = C⊽U; (C⊽V)⊽(U⊽V) |
| ¬((A⊻B)⊻C) | 0 or 2 | 1,0,0,1,0,1,1,0 | 9 | 6 | T = A⊼B; U = (A⊼T)⊼(B⊼T); (C⊼U)⊼(¬C⊼¬U) | 9 | 6 | T = A⊽B; U = (A⊽T)⊽(B⊽T); (C⊽U)⊽(¬C⊽¬U) |
| ((A⊻B)⊻C) ∨ ¬(A∨B∨C) | not 2 | 1,1,1,0,1,0,0,1 | 8 | 4 | T = A⊼B; [(B⊼T) ⊼ (A⊼(B⊼C))] ⊼ (¬C⊼T) | 10 | 5 | T = ¬A; U = ¬B; V = C⊽(T⊽U); [((A⊽U)⊽(B⊽T)) ⊽ V] ⊽ (C⊽V) |
| ((A⊻B)⊻C) ∧ ¬(A∧B∧C) | 1 | 0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0 | 10 | 5 | T = ¬A; U = ¬B; V = C⊼(T⊼U); [((A⊼U)⊼(B⊼T)) ⊼ V] ⊼ (C⊼V) | 8 | 4 | T = A⊽B; [(B⊽T) ⊽ (A⊽(B⊽C))] ⊽ (¬C⊽T) |
Note: I may have missed optimal solutions for the most complex formulas because these are the largest exhaustive searches I have made:
- any number of NAND gates and maximum delay 4
- up to 9 NAND gates and maximum delay 5
- up to 7 NAND gates and maximum delay 6
That is, there may be a solution with 8 NAND gates for ¬((A⊻B)⊻C).
Order of inputs matters
| Formula | Truth table | NAND and NOT gates only | NOR and NOT gates only | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gates | Delay | Formula | Gates | Delay | Formula | ||
| (A∧B)∨¬C | 1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1 | 2 | 2 | (A⊼B)⊼C | 4 | 3 | T = ¬C; (A⊽T)⊽(B⊽T) |
| (A∨B)∧¬C | 0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0 | 4 | 3 | T = ¬C; (A⊼T)⊼(B⊼T) | 2 | 2 | (A⊽B)⊽C |
| (A∧B)∨C | 0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1 | 3 | 2 | (A⊼B)⊼¬C | 3 | 2 | (A⊽C)⊽(B⊽C) |
| (A∨B)∧C | 0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1 | 3 | 2 | (A⊼C)⊼(B⊼C) | 3 | 2 | (A⊽B)⊽¬C |
| (A∧¬B)∨¬C | 1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0 | 3 | 3 | (A⊼¬B)⊼C | 5 | 3 | T = ¬C; (A⊽T)⊽(¬B⊽T) |
| (A∨¬B)∧¬C | 1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0 | 5 | 3 | T = ¬C; (A⊼T)⊼(¬B⊼T) | 3 | 3 | (A⊽¬B)⊽C |
| (A∧¬B)∨C | 0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1 | 4 | 3 | (A⊼¬B)⊼¬C | 4 | 3 | (A⊽C)⊽(¬B⊽C) |
| (A∨¬B)∧C | 0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1 | 4 | 3 | (A⊼C)⊼(¬B⊼C) | 4 | 3 | (A⊽¬B)⊽¬C |
| A∨¬B∨¬C | 1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1 | 4 | 3 | ¬A⊼¬(B⊼C) | 6 | 5 | ¬(¬(A⊽¬B)⊽¬C) |
| A∧¬B∧¬C | 0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0 | 6 | 5 | ¬(¬(A⊼¬B)⊼¬C) | 4 | 3 | ¬A⊽¬(B⊽C) |
| A∧B∧¬C | 0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0 | 5 | 4 | ¬(¬(A⊼B)⊼¬C) | 5 | 4 | ¬(¬A⊽¬B)⊽C |
| A∨B∨¬C | 1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1 | 5 | 4 | ¬(¬A⊼¬B)⊼C | 5 | 4 | ¬(¬(A⊽B)⊽¬C) |
4-input gates
The truth tables show the output of the function for all combinations of the inputs: A=0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1; B=0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1; C=0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1; D=0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1. These formulas may not be optimal.
Order of inputs does not matter
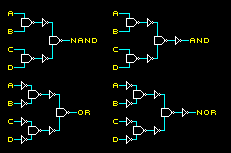
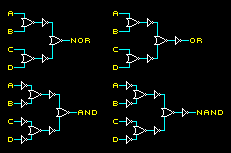
(TODO: redraw diagrams)
| Formula | A+B+C+D must equal | Truth table | NAND and NOT gates only | NOR and NOT gates only | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gates | Delay | Formula | Gates | Delay | Formula | |||
| ¬(A∧B∧C∧D) | not 4 | 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0 | 5 | 3 | ¬(A⊼B)⊼¬(C⊼D) | 10 | 5 | ¬(¬(¬A⊽¬B)⊽¬(¬C⊽¬D)) |
| ¬(A∨B∨C∨D) | 0 | 1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0 | 10 | 5 | ¬(¬(¬A⊼¬B)⊼¬(¬C⊼¬D)) | 5 | 3 | ¬(A⊽B)⊽¬(C⊽D) |
| A∧B∧C∧D | 4 | 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1 | 6 | 4 | ¬(¬(A⊼B)⊼¬(C⊼D)) | 9 | 4 | ¬(¬A⊽¬B)⊽¬(¬C⊽¬D) |
| A∨B∨C∨D | not 0 | 0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 | 9 | 4 | ¬(¬A⊼¬B)⊼¬(¬C⊼¬D) | 6 | 4 | ¬(¬(A⊽B)⊽¬(C⊽D)) |
Order of inputs matters
| Formula | Truth table | NAND and NOT gates only | NOR and NOT gates only | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gates | Delay | Formula | Gates | Delay | Formula | ||
| ¬(A∧B∧C∧¬D) | 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1 | 6 | 4 | ¬(A⊼B) ⊼ ¬(C⊼¬D) | 9 | 5 | ¬(¬(¬A⊽¬B) ⊽ ¬(¬C⊽D)) |
| ¬(A∨B∨C∨¬D) | 0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0 | 9 | 5 | ¬(¬(¬A⊼¬B) ⊼ ¬(¬C⊼D)) | 6 | 4 | ¬(A⊽B) ⊽ ¬(C⊽¬D) |
| A∨B∨¬C∨¬D | 1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 | 7 | 4 | ¬(¬A⊼¬B) ⊼ ¬(C⊼D) | 8 | 5 | ¬(¬(A⊽B) ⊽ ¬(¬C⊽¬D)) |
| A∧B∧¬C∧¬D | 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0 | 8 | 5 | ¬(¬(A⊼B) ⊼ ¬(¬C⊼¬D)) | 7 | 4 | ¬(¬A⊽¬B) ⊽ ¬(C⊽D) |
| A∧B∧C∧¬D | 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0 | 7 | 5 | ¬(¬(A⊼B) ⊼ ¬(C⊼¬D)) | 8 | 4 | ¬(¬A⊽¬B) ⊽ ¬(¬C⊽D) |
| A∨B∨C∨¬D | 1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 | 8 | 4 | ¬(¬A⊼¬B) ⊼ ¬(¬C⊼D) | 7 | 5 | ¬(¬(A⊽B) ⊽ ¬(C⊽¬D)) |
RPN calculator
This command-line Python program accepts a formula in Reverse Polish notation (RPN) and prints the corresponding truth table. In RPN, operands precede their operator; the advantage is that parentheses are not needed. For example, A¬B¬⊼¬ is equivalent to ¬((¬A)⊼(¬B)) in ordinary notation. The truth table consists of output bits of the formula when it is evaluated for every possible combination of the input bits.
Command line arguments:
- number of input bits (1–8)
- formula
The program has an internal stack. For each evaluation of the formula, the stack starts empty and is affected by operands and operators. The stack must contain exactly one bit at the end of the formula. You can't pop from an empty stack.
The formula may include these symbols:
- operands (push a bit to the stack):
- constant:
0, 1 - input bit (corresponding to current combination of input bits):
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H(the “number of input bits” argument determines which can be used)
- constant:
- operators (pop one or more bits and push the result):
- unary (pop 1 bit and push 1):
¬(NOT) - binary (pop 2 bits and push 1):
∧, ⊼, ∨, ⊽, ⊻(AND, NAND, OR, NOR, XOR)
- unary (pop 1 bit and push 1):
- spaces (ignored)
E.g. python3 rpncalc.py 2 "A¬B¬⊼¬" will print 1,0,0,0.